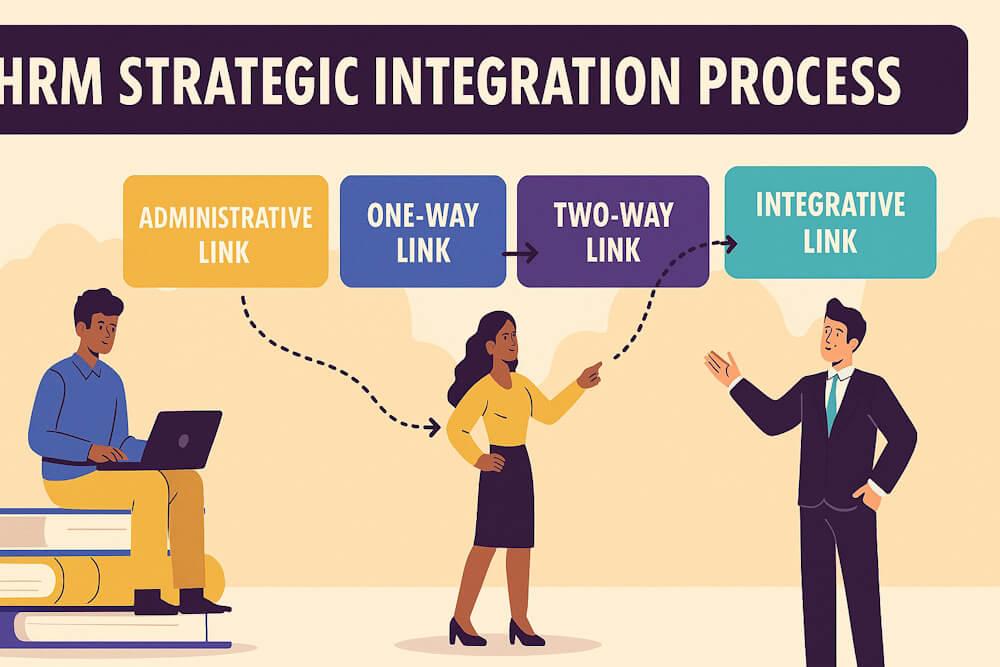
Introduction
In the 21st century, one of the most important jobs for HR managers is to plan for human resources (HR). The HR function has changed from working "behind the scenes" to being a major factor in how well an organization does. HR jobs have become more strategic because of globalization, advances in technology, and changing expectations from workers.
Managing people today is harder than ever, and it requires specialized knowledge and flexible plans. Global changes like mass layoffs and high unemployment have made HR professionals rethink how they hire people, plan their workforces, and keep employees interested (Zorlu, 2009).
I. Hiring and Choosing
The basis of good HR management is hiring and choosing the right people. Miller and Cardy (2000) say that HR's main job is to find and hire people who have the right skills and attitude for the company to grow.
But globalization has made hiring more difficult by making talent pools available across borders. This opens up new possibilities, but it also brings up problems, like communication problems between recruiters and hiring managers and higher advertising costs.
Also, hiring decisions can be affected by biases and cultural perceptions. In today's diverse workplace, HR professionals should not focus on things like where someone comes from, their race, or their values. Instead, they should focus on their skills, how well they can adapt, and how well they fit in with the culture. In an environment that is becoming more competitive, both multinational and local companies have trouble finding and keeping qualified workers.
II. Growth and Development in Your Career
Employee career advancement activities are measures performed by both companies and employees to improve their knowledge and stay current with current events.
Globalization has resulted in numerous technological advancements. Innovation is the most important factor in any business's ability to expand and thrive. Internal career progression possibilities can assist firms retain top talent by preventing them from looking for work elsewhere. It is critical to train and develop employees so that they can deal with all of the changes and advancements that will come their way.
Nowadays, training should not be confined to teaching employees a single skill or information; rather, it should focus on the employees' overall growth and career development. The training should not be done only for the sake of it; the content of the training programme must also be carefully considered.
III. Encouraging a Positive Workplace Culture and Managing a Diverse Workforce
Diverse and multicultural workforces are a common feature of modern businesses. This diversity fosters creativity and innovation, yet necessitates meticulous cultural integration.
One of the hardest things for HR to do is to build and keep a strong company culture that brings together employees from different backgrounds. As mergers and acquisitions become more common in the 21st century, HR managers need to create a culture that values teamwork, inclusion, and shared values (Williams, 2003).
A clear organizational culture makes employees more loyal and makes sure that everyone is on the same page with the company's mission and vision.
IV. Dealing with and Resolving Conflicts
Conflict is a normal part of working in an organization. It can be helpful, leading to new ideas and better work, or harmful, hurting relationships and productivity.
Conflict management is now an important part of HR in today's high-pressure workplaces, where long hours, competition, and deadlines are common. HR managers need to be mediators to make sure that disagreements are settled quickly and fairly. They also help with communication between management and labor unions, dealing with complaints, and making sure everyone knows the rules of behavior.
For HR professionals to be able to resolve conflicts well, they need to be open, compassionate, and good at communicating.
V. Corporate Values and Business Ethics
In today's business world, morals and values are very important for long-term success. HR departments must always be honest and fair because of changes in the workplace culture, leadership styles, and technology.
HR has to deal with ethical problems a lot because it works directly with employees. These problems include discrimination, privacy of data, and being open about how well employees are doing. If an organization doesn't follow ethical standards, it can hurt its reputation and slow its growth. So, one of HR's most important jobs is to create a culture of honesty and responsibility.
VI. Running a Workforce with People from Different Generations
There are people from different generations working together in the 21st century. Baby Boomers, Generation X, and Generation Y (Millennials) all have different values and ways of working.
- Baby Boomers tend to like stable, traditional work environments.
- People in Generation X and Y are usually tech-savvy, adaptable, and willing to try new ways of working.
HR managers need to find a balance that uses the best parts of each generation. Organizations can improve collaboration, productivity, and innovation by recognizing these differences and making policies that include everyone.
To handle this kind of diversity, HR needs to create personalized communication, motivation, and training programs that meet the needs of different generations.
VII. Ways to Keep People Motivated and Keep Them on the Job
Keeping employees has become a big problem in a global job market. It's hard for companies to keep their employees loyal when they have a lot of career options.
To fix this, HR managers need to come up with new ways to motivate people that don't involve money. Today's workers want to be recognized, do work that matters, and have chances to move up in their careers. Companies can keep more employees by giving them flexible work hours, rewards based on performance, mentorship programs, and a friendly work environment (Henson, 2007).
To keep employees interested and happy, it's important to focus on both intrinsic and extrinsic motivators.
VIII. Managing the 5 R's of HRM
The 5 R's framework is becoming more and more important for HR success in the 21st century:
- Resourcing means figuring out what the future workforce will need.
- Recruiting means finding and hiring the right people.
- Retaining means keeping top performers interested.
- Retraining means giving employees new skills so they can deal with changes.
- Restructuring means changing the way an organization is set up to meet its changing goals.
HR leaders can make sure that their organizations are flexible and can grow over time in a changing business world by effectively managing these five areas.
In Conclusion
In the 21st century, HR does a lot more than just administrative work. It now includes strategic planning, helping employees grow, leading with integrity, and changing the organization.
HR professionals need to keep up with changes around the world, use technology, and make policies that put people first and balance productivity with employee health. The future of HRM depends on being able to connect human potential with business goals, learn new things all the time, and understand different cultures.