Whenever the government changes the GST rate — whether it’s an increase or a reduction — one common confusion pops up everywhere:
- “Which GST rate should I apply — the old one or the new one?”
- “What if invoice and payment fall on different dates?”
- “What if goods were supplied earlier but invoicing happened after rate change?”
This is exactly why Section 14 of the CGST Act exists. It lays down special rules for determining the Time of Supply (TOS) in case of a change in GST rate.
This blog explains everything in the smoothest way possible — with clean examples and practical situations so you can apply the concept instantly.
Why Section 14 Exists
Normally under GST:
- For goods → Section 12 applies
- For services → Section 13 applies
But these sections don’t solve the biggest problem during rate changes:
When different pieces of a transaction (invoice, supply, payment) fall on opposite sides of the tax-rate-change date.
To ensure fairness — and prevent confusion — Section 14 gives a special “matrix-based” rule.
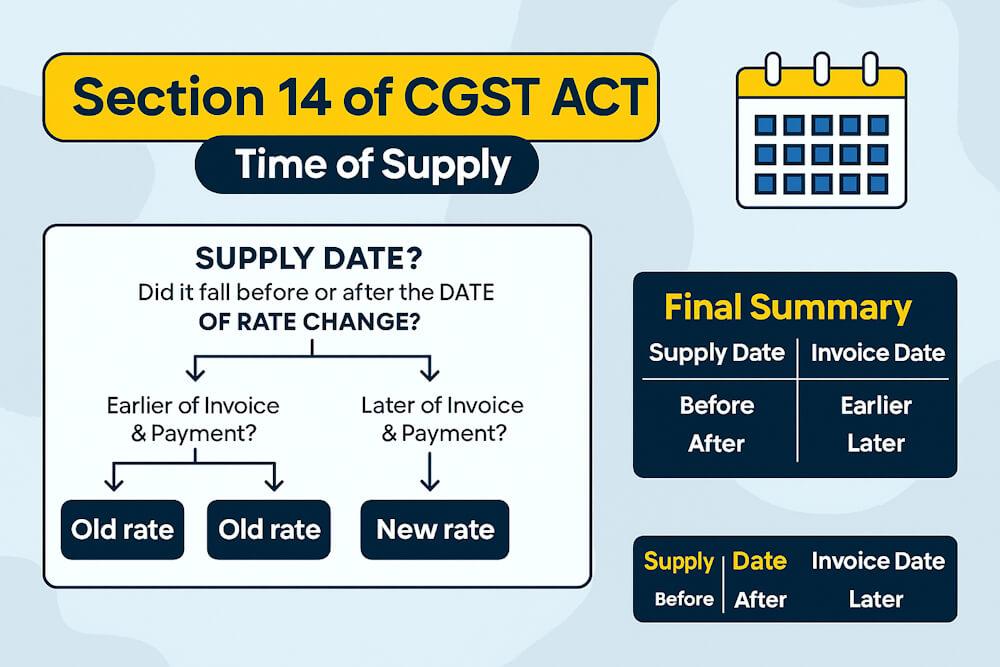
Core Idea of Section 14 (Easy Version)
GST rate depends on two things:
- When the supply happened, and
- When invoice/payment happened
If supply is before the rate change → Section 14 treats invoice/payment differently. If supply is after the rate change → again different logic applies.
Let’s break this down.
The Date Everything Revolves Around
This magic date is called:
“Date of Change in GST Rate”
Let’s call it: R = Rate Change Date
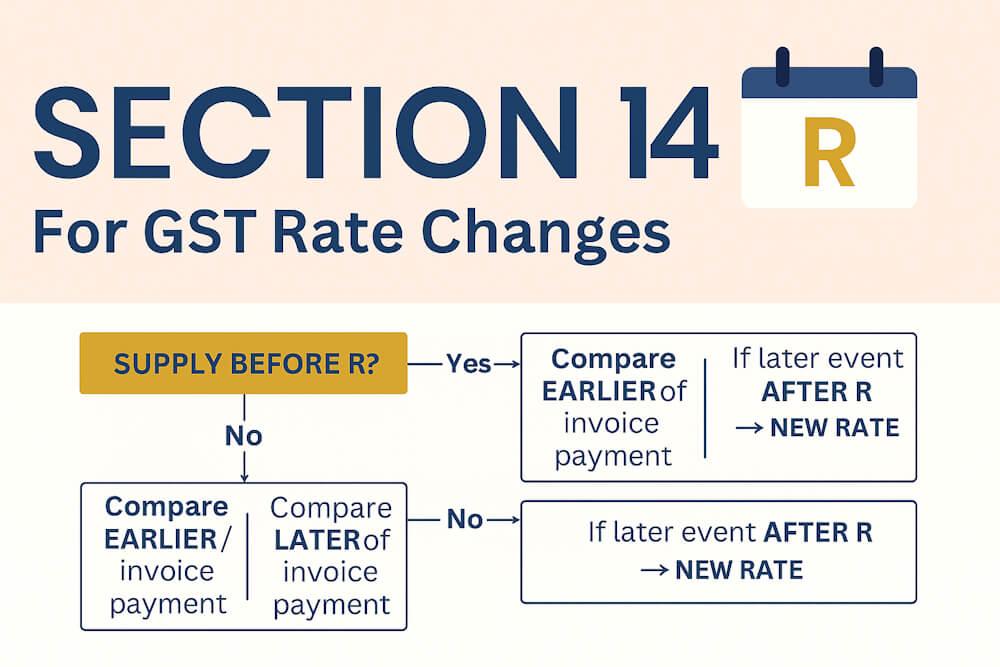
Everything in Section 14 revolves around whether:
- Supply happened before R
- Invoice/payment happened before or after R
Once you understand this, the entire section becomes a simple chart.
Section 14 Is Divided Into Two Main Parts
- Part A – Supply is BEFORE rate change
- Part B – Supply is AFTER rate change
Each part has 3 sub-scenarios based on invoice/payment.
Let’s go step-by-step.
PART A – Supply BEFORE Rate Change
👉 If supply happened before R, then:
| Scenario | Invoice | Payment | GST Rate to Apply |
| 1 | After R | After R | New Rate |
| 2 | Before R | After R | Old Rate |
| 3 | After R | Before R | Old Rate |
Golden Rule for Part A (Supply Before Rate Change):
GST rate = whichever event (invoice or payment) happens earlier, and if that earlier event is before R → old rate applies.
Example A1 – Supply Before, Invoice & Payment After R
Old rate: 12% New rate: 18% Rate change date: 1 July
- Supply: 25 June
- Invoice: 10 July
- Payment: 15 July
Both events are after rate change
- GST = 18% (new rate)
Example A2 – Supply Before, Invoice Before, Payment After R
- Supply: 20 June
- Invoice: 25 June
- Payment: 10 July
Earliest event = invoice date (before rate change)
- GST = old rate (12%)
Example A3 – Supply Before, Invoice After, Payment Before R
- Supply: 22 June
- Invoice: 5 July
- Payment: 28 June
Earliest event = payment date (before R)
- GST = old rate
PART B – Supply AFTER Rate Change
If supply happened after R:
| Scenario | Invoice | Payment | GST Rate to Apply |
| 4 | Before R | Before R | Old Rate |
| 5 | Before R | After R | New Rate |
| 6 | After R | Before R | New Rate |
Golden Rule for Part B:
GST rate = later of invoice/payment. If that later event is after R → new rate applies.
Notice how this is the opposite of Part A.
Example B1 – Supply After, Invoice & Payment Before R
- Supply: 5 July
- Invoice: 28 June
- Payment: 29 June
Latest event = 29 June (before R)
- GST = old rate
Example B2 – Supply After, Invoice Before, Payment After R
- Supply: 6 July
- Invoice: 28 June
- Payment: 4 July
Latest event = payment, which is after R
- GST = new rate
Example B3 – Supply After, Invoice After, Payment Before R
- Supply: 8 July
- Invoice: 12 July
- Payment: 25 June
Latest event = invoice (after R)
- GST = new rate
The Full Section 14 Logic in One Simple Diagram
Why Supply Date Matters the Most
The law assumes:
- If supply is before R, the old rate should ideally apply
- If supply is after R, the new rate should ideally apply
But since invoice/payment can happen at different times, Section 14 creates a fair method to align everything.
Real-Life Practical Scenarios
Scenario 1 – Contractor Work Across Rate Change
- Govt increases GST rate from 12% → 18%
- Contractor completes 80% of job before R
- Invoice raised after R
Supply before R → invoice after R Earlier event? Payment is earlier? GST depends on timing accordingly.
Scenario 2 – Sale of Machinery
- Dispatch on 28 June
- Invoice on 2 July
- Payment on 30 June
Supply before R Earlier event = payment → before R
- Old rate
Scenario 3 – Yearly Subscription Service
Subscription is renewed annually.
- Renewal date: 10 July
- Customer pays in advance on 25 June
Supply after R Later event = supply (10 July)
- New rate applies
Scenario 4 – Professional Fees
- Work completed: 20 June
- Invoice: 5 July
- Payment: 12 July
Both events after R
- new rate
One More Easy Table to Remember
When supply is before R → take EARLIER of invoice/payment
When supply is after R → take LATER of invoice/payment
That’s all. Entire Section 14 fits into these two lines.
Common Mistakes Businesses Make
- Using invoice date alone = Section 14 overrides the usual rules.
- Ignoring supply-completion date = This is the first thing you must determine.
- Adjusting invoices after rate change = Wrong if supply occurred before R.
- Believing advance payments always use old rate = Not always — depends on supply timing.
- Thinking both goods and services have different rules = Section 14 applies to both.
FAQ
- Q. What is supply date for goods? = Usually the date of removal/dispatch.
- Q. What is supply date for services? = Date service is completed or performance milestone achieved.
- Q. What if invoice and payment both after R? = New rate applies — regardless of supply date.
- Q. Does Section 14 override Section 12 & 13? = Yes, only when there is a change in rate.
Final Summary
| Supply Timing | Invoice | Payment | Rate |
| Before R | After | After | New |
| Before R | Before | After | Old |
| Before R | After | Before | Old |
| After R | Before | Before | Old |
| After R | Before | After | New |
| After R | After | Before | New |
Once you understand these patterns, rate change situations become very simple to apply.