Getting a GST registration is one thing, but maintaining it correctly is just as important. Many businesses eventually reach a point where they either shut down, change their structure, stop making taxable supplies, or simply don’t need a GST number anymore. In other cases, the GST department may cancel a registration due to non-compliance.
That’s where Section 29 of the CGST Act comes in. It deals with cancellation of GST registration, either:
- Voluntarily (applied by the taxpayer), or
- Compulsorily (done by the officer).
This blog breaks down everything you need to know about when GST can be cancelled, what the law says, how the process works, and what happens after cancellation.
What Is Cancellation of GST Registration?
GST cancellation means your GSTIN becomes inactive and you can no longer:
- Collect GST
- Issue GST invoices
- Claim input tax credit (ITC)
- File regular GST returns
Cancellation is required when:
- Business closes
- You are no longer liable to be registered
- Business is transferred
- Turnover is below threshold
- Person wishes to stop GST compliance
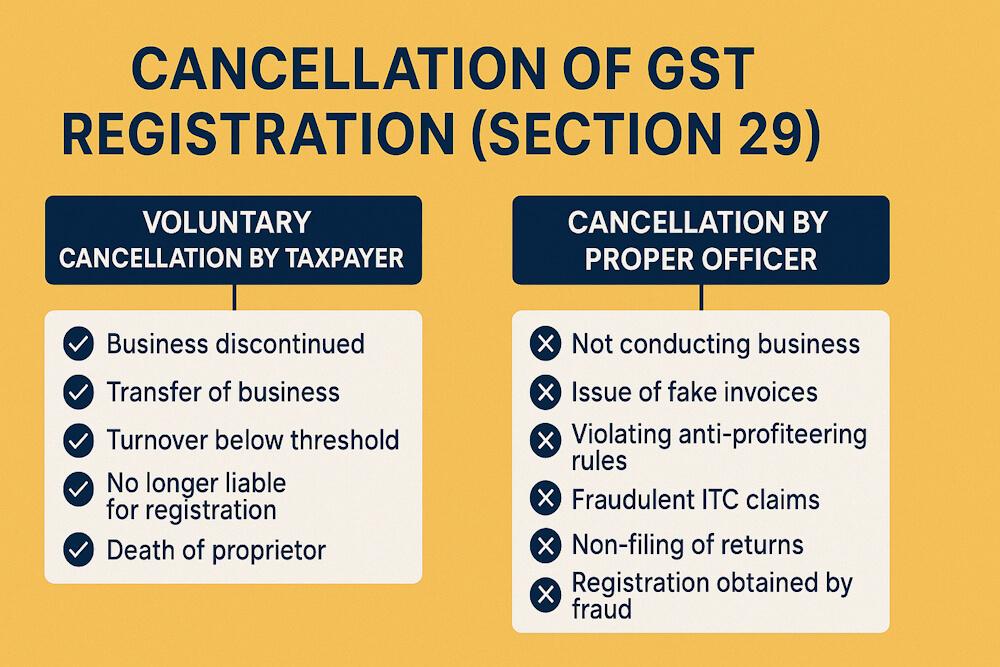
Types of GST Cancellation Under Section 29
There are two types:
Voluntary Cancellation by Taxpayer
You can apply for cancellation yourself in cases like:
- Business is discontinued
- You are no longer liable for registration
- Turnover drops below threshold
- Switching to unregistered business
- Change in PAN (due to merger, demerger, etc.)
- Transfer of business to another person
- Death of sole proprietor
Cancellation by Proper Officer (Compulsory Cancellation)
The GST officer may cancel your registration if you violate:
- Non-filing of returns
- Fake invoices
- Fraudulent ITC claims
- Wrong registration obtained
- Not conducting business at registered address
- Supplying goods/services without GST invoice
- E-way bill non-compliance
- Inactive business for long period
Officer cancellation is common when businesses don’t file returns for 6+ months.
Section 29 – Detailed Explanation
- Section 29(1) covers voluntary cancellation.
- Section 29(2) covers compulsory cancellation.
- Section 29(3) covers liability after cancellation.
Grounds for Voluntary Cancellation (Section 29(1))
You may apply for cancellation when:
Business is discontinued or closed
Example: A bakery owner shuts down operations permanently.
Transfer of business
When business is sold, merged, demerged, or transferred.
Change in constitution of business
E.g.: Partnership firm converts into LLP.
Turnover drops below threshold limit
A trader falls below ₹40 lakh limit (goods).
No longer making taxable supplies
You shift from taxable services to exempt services.
Death of proprietor
Legal heir applies for cancellation.
Grounds for Compulsory Cancellation (Section 29(2))
The officer may cancel GST registration if:
1. Person does not conduct business from registered premises
E.g., address fake or vacant.
2. Issues invoices without actual supply (Fake invoicing)
Common fraud under GST.
3. Violates anti-profiteering rules
Not passing benefits of reduced tax to customers.
4. Claiming ITC fraudulently
Taking credit without receiving goods/services.
5. Does not file returns for long duration
E.g.:
- Normal taxpayer → Not filed for 6 months
- Composition taxpayer → Not filed for 3 quarters
6. Uses GST for illegal activities
E.g., bogus companies formed only to claim ITC.
7. Obtains registration through misrepresentation or fraud
Suspension of Registration Before Cancellation
Before final cancellation, the officer may first suspend your registration.
Suspension means:
- Cannot issue invoices
- Cannot file returns
- Cannot claim ITC
- Business legally paused
Suspension gives time for investigation.
Form Used for Cancellation
There are three main forms:
| Purpose | GST Form |
| Apply for cancellation | REG-16 |
| Officer issues Show Cause Notice | REG-17 |
| Reply by taxpayer | REG-18 |
| Cancellation order | REG-19 |
| Revocation after cancellation | (covered in Blog 11) |
Procedure for Voluntary Cancellation (REG-16)
Here’s the step-by-step process:
Step 1: Login to GST portal
Go to → Services → Registration → Application for Cancellation
Step 2: Select Reason for Cancellation
Options include:
- Closure of business
- Change in constitution
- Transfer of business
- No longer liable to register
- Others
Step 3: Furnish Required Details
You must provide:
- Date of closure
- Details of stock
- Liabilities
- ITC reversal amount
- Tax payable on stock
- Supporting documents
Step 4: ITC Reversal Requirement
You must reverse input tax credit on:
- Inputs
- Capital goods
- Stock
- Finished goods
ITC reversal = higher of:
- ITC in stock
- GST on stock value
Step 5: Verification & Submission
Submit application through:
- DSC
- EVC OTP
- Aadhaar E-sign
Step 6: Cancellation Order (REG-19)
Officer approves → GSTIN cancelled.
A cancellation certificate is issued.
Procedure for Compulsory Cancellation
If officer wants to cancel your GSTIN:
Step 1: Officer issues Show Cause Notice (REG-17)
SCN mentions reason for proposed cancellation.
Step 2: Taxpayer replies via REG-18
Reply must be given within 7 days.
Step 3: Officer decision
- Accept reply → No cancellation
- Reject reply → Pass cancellation order (REG-19)
Liability After Cancellation (Section 29(3))
Even after cancellation:
You must pay:
- Tax on closing stock
- ITC reversal
- Pending returns
- Penalties (if any)
GST liability does NOT automatically disappear.
Effects of Cancellation
Once cancelled:
- Cannot legally operate using GSTIN
- Cannot issue tax invoices
- Cannot collect GST from customers
- Cannot claim ITC
Must file final return – GSTR-10
Who Must File GSTR-10?
Only those whose GST registration is cancelled or surrendered.
Not required for:
- TDS/TCS deductors
- UIN holders
Input Tax Credit (ITC) Impact After Cancellation
Once cancelled:
- ITC becomes invalid
- Unused ITC must be reversed
- Input credit cannot be claimed for future supplies
Cancellation Vs Revocation
- Cancellation = GSTIN becomes inactive
- Revocation = Restores cancelled GSTIN
Real Examples to Understand Section 29
Example 1: Business Closed Permanently
- A shop owner shuts down his business.
- He applies for cancellation voluntarily.
- Officer approves.
Example 2: Non-Filing of Returns
- A trader has not filed GSTR-3B for 1 year.
- Officer issues REG-17 → Cancels GSTIN.
Example 3: Fake Invoices
- A company claims ITC without receiving goods.
- GSTIN cancelled for fraud.
Example 4: Transfer of Business
A sole proprietor dies. Legal heir applies for cancellation.
Example 5: Threshold Falls Below Limit
Service provider's turnover drops to ₹8 lakh. He applies for cancellation.
Common Mistakes Taxpayers Make
- Ignoring SCN notice
- Not filing GSTR-10
- Not reversing ITC
- Forgetting to cancel GSTIN after closure
- Providing unclear documents
- Using GSTIN after cancellation (illegal)
Conclusion
Section 29 of the GST Act ensures that businesses who shut down, restructure, or become non-operational can exit the GST system smoothly. At the same time, it empowers GST authorities to cancel registrations of non-compliant businesses.
Understanding the cancellation process helps avoid penalties, stay compliant, and maintain a clean tax status.
FAQs
1. What is GST cancellation under Section 29?
It is the process of deactivating a GSTIN due to closure, turnover change, transfer, or violations.
2. How do I cancel my GST registration voluntarily?
Submit REG-16 with details like reason, stock, ITC reversal, and closure date.
3. What is compulsory cancellation?
Cancellation initiated by officer due to non-filing, fraud, address mismatch, or misuse of GST.
4. What happens after GST cancellation?
You must file GSTR-10 and reverse ITC. GSTIN becomes inactive.
5. Can a cancelled GST number be restored?
Yes, through revocation (covered in Section 30).
6. What is REG-17?
A show cause notice for proposed cancellation.
7. Is filing GSTR-10 mandatory?
Yes, for all cancelled registrations.