Globalization symbolizes the free flow of technology, capital, and human resources across national boundaries, creating a dynamic and highly competitive business environment. It is a process that connects people worldwide through advanced communication technologies, effectively transforming the global business landscape.
This transformation has had a profound impact on Human Resource Management (HRM). Today, HR professionals must manage people across countries, cultures, and legal systems, making international HRM more complex and strategic than ever before.
Global Talent and the “Think Global, Act Local” Approach
Earlier, HR managers relied on limited local labor markets to meet organizational needs. Globalization has changed this completely. Organizations can now recruit talent from any part of the world, allowing access to diverse skills, ideas, and perspectives.
The future success of organizations depends on their ability to manage a diverse global workforce, encouraging innovation while maintaining harmony. As a result, HR managers increasingly follow the principle of:
“Think Global, Act Local.”
This approach helps balance global consistency with local adaptation.
Cultural Diversity and HR Challenges
HR managers today must undergo cross-cultural training to manage highly skilled yet culturally diverse employees. They must also ensure that local employees do not perceive foreign talent as a threat to career growth.
The effectiveness of diversity management depends on the HR manager’s ability to balance:
- Cultural sensitivity
- Employee motivation
- Organizational objectives
Global workforce diversity makes HRM both challenging and rewarding.
Impact of Global Expansion on HRM Practices
When organizations expand into foreign markets, globalization significantly influences HR development and management. Companies must adapt HR practices to:
- Hire and retain employees across countries
- Provide cross-cultural and language training
- Support geographically dispersed teams
- Comply with foreign regulations
HR departments must continuously update policies to align with cultural differences, legal requirements, and technological advancements.
Globalization of Human Capital
Human capital is the most valuable asset for any organization. As companies expand globally, HR policies must support both existing and newly hired employees.
HR responsibilities include:
- Visa and work permit assistance
- Relocation and housing support
- Cultural and language training
- Development of local talent
In some cases, firms rely on local employees, while in others they transfer experienced employees abroad. Employee mobility becomes a key productivity factor.
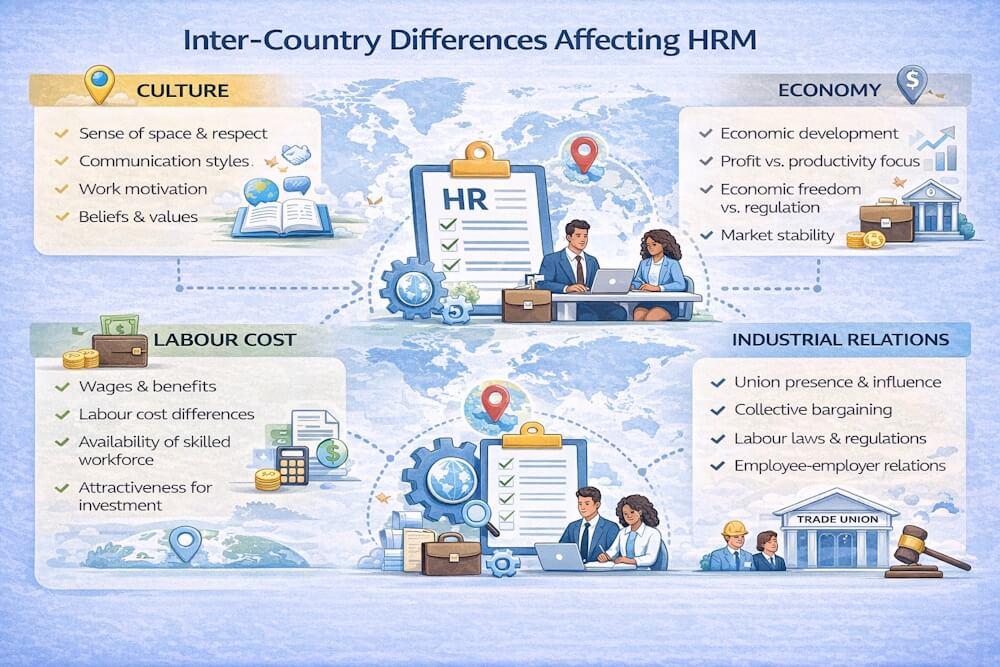
Corporate and Cultural Differences
Every organization has a unique corporate culture, but globalization exposes firms to societal and cultural differences that influence employee behavior and expectations.
Cultural norms affect:
- Work-life balance
- Gender roles in leadership
- Working hours and schedules
- Management styles
For example, while female leadership is common in some countries, it may not be culturally accepted elsewhere. Similarly, managers from headquarters may struggle abroad if they fail to understand local business practices.
Managers who adapt to local cultures tend to achieve better employee cooperation and performance.
Employment and Tax Laws
Global operations expose firms to diverse labor and tax laws. HR departments must manage:
- Different tax systems
- Employment contracts
- Leave policies and benefits
- Environmental and labor regulations
Compliance often requires modifying existing corporate HR policies to align with host-country laws. HR managers must stay informed about changing regulations across countries.
Long-Distance Communication Challenges
Global HRM involves managing employees across multiple time zones and locations. Face-to-face interaction is often replaced by:
- Emails
- Video conferencing
- HR management systems
Language barriers and time differences can delay issue resolution, making communication a major HR challenge in global organizations.
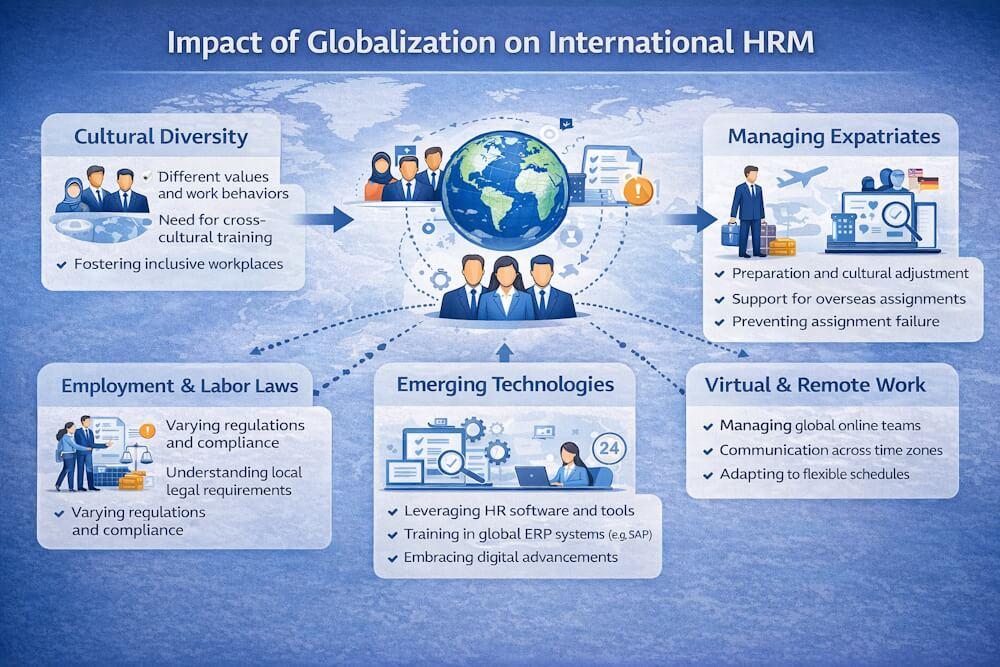
Key Impacts of Globalization on International HRM
1. Increased Cultural Diversity
Globalization has diversified the workforce, requiring new HR policies and practices. Cultural differences in communication, perception, and work behavior increase HR complexity but also bring valuable insights.
2. Differences in Employment Laws
Labor laws vary significantly across countries. HR policies must address both monetary and non-monetary benefits such as flexible working hours and leave structures.
3. Managing Expatriates
Preparing employees for international assignments requires cultural training, motivation, and continuous support. Expatriate success directly impacts business performance.
4. Improved Workplace Standards
Global firms have raised safety and working condition standards, especially in developing countries. This has led to better labor practices and reduced child labor in many regions.
5. Managing Virtual Employees
Globalization has increased remote and on-site client-based roles. Managing virtual employees requires different engagement, retention, and performance strategies.
6. Flexible Working Hours
Working across time zones has led to flexible schedules, supporting work-life balance and employee retention, especially for women employees.
7. Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
CSR initiatives help firms build a positive image in host countries. Employee involvement in CSR reduces stress and improves organizational commitment.
8. Adapting to Emerging Technologies
Employees are trained in global systems like ERP (SAP, PeopleSoft) and quality tools such as Six Sigma, enabling them to operate efficiently on international platforms.
9. Shift from Subordinates to Business Partners
Globalization has transformed employees into business partners, where each individual contributes directly to organizational growth and success.
FAQs
What is globalization in HRM?
Globalization in HRM refers to managing human resources across national boundaries while addressing cultural, legal, and technological differences.
How does globalization affect international HRM?
It increases workforce diversity, expatriate management challenges, compliance complexity, and reliance on technology for communication.
Why is cultural diversity a challenge for HR managers?
Different values, languages, and work behaviors require customized HR policies and cross-cultural training.
What role does HRM play in global organizations?
HRM supports talent acquisition, employee development, legal compliance, and organizational integration across countries.
How does globalization improve HR practices?
It encourages flexible work arrangements, higher workplace standards, skill development, and employee empowerment.