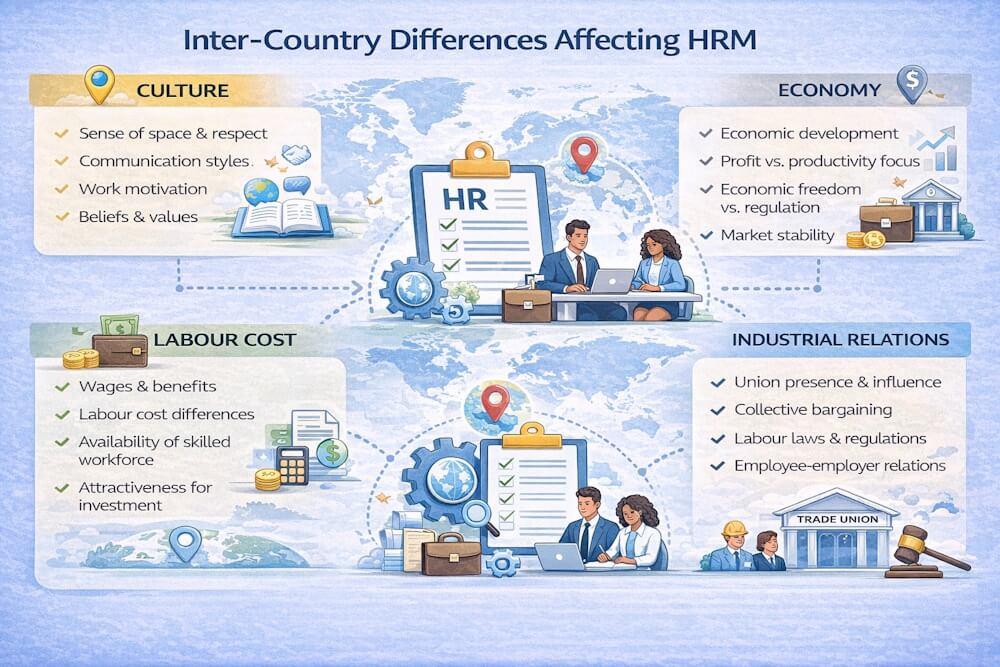
As organizations expand beyond national boundaries, inter-country differences become a critical factor influencing human resource management (HRM) practices. Policies that work effectively in one country may fail in another due to differences in culture, economic conditions, labour costs, and industrial relations systems.
Understanding and adapting to these differences is essential for managing a global workforce successfully.
The four major inter-country differences that affect HRM are:
- Cultural factors
- Economic factors
- Labour cost factors
- Industrial relations factors
1. Cultural Factors
Culture plays a central role in shaping workplace behaviour, management style, communication patterns, and employee expectations. Each country has a distinct cultural framework that influences how business is conducted.
Key Cultural Elements Affecting HRM
- Sense of space and respect
- Greeting and addressing habits
- Appearance and dress codes
- Language and communication styles
- Time orientation and punctuality
- Motivation and work attitudes
- Beliefs and value systems
Cross-Country Cultural Differences
For example:
- Power distance is lower in the United States compared to countries such as China, Russia, and France.
- The United States ranks high in individualism, whereas many Asian countries, including India, emphasize collectivism.
- The US workforce is generally more flexible and adaptable to change, while countries like Japan, Russia, and France may exhibit greater resistance to change.
These cultural differences significantly influence recruitment, leadership style, performance appraisal, training, and employee engagement practices.
2. Economic Factors
Economic factors relate to how countries manage their economic systems and define business objectives.
Some countries prioritize:
- Profit maximization
- Shareholder value
Others focus more on:
- Productivity
- Efficiency
- Employment generation
The economic condition and level of economic freedom also shape HR policies such as compensation, benefits, and employment security.
Examples of Economic Freedom Levels
- High economic freedom: Hong Kong, Singapore, Australia, Canada
- Low economic freedom: Iran, Zimbabwe, North Korea
Countries with higher economic freedom typically offer more flexible labour markets, whereas restricted economies impose stricter employment regulations affecting HRM practices.
3. Labour Cost Factors
Labour cost refers to the total expenditure incurred by an organization on employees, including:
- Wages
- Benefits
- Insurance
- Social security contributions
Labour cost differences strongly influence international location decisions and HR policies.
Comparative Labour Costs (Approximate)
- India: $0.48 per hour
- Vietnam: $0.39 per hour
- Bangladesh: $0.23 per hour
Lower labour costs often attract multinational enterprises seeking cost advantages. However, these differences also require adjustments in HR policies related to compensation structures, working conditions, and employee retention.
4. Industrial Relations Factors
Industrial relations refer to the relationship between:
- Employers
- Employees
- Trade unions
This relationship significantly affects HRM practices such as:
- Collective bargaining
- Dispute resolution
- Wage determination
- Employee participation
The role and strength of trade unions vary widely across countries.
Examples of Strong Trade Union Influence
- China – All-China Federation of Trade Unions
- South Africa – Congress of South African Trade Unions
- France – General Confederation of Labour
- Germany – IG Metall
In countries with strong union presence, HR managers must engage actively with unions and comply with collective agreements, whereas in less unionized environments, HR policies are more management-driven.
Impact of Inter-Country Differences on HRM
Inter-country differences affect almost every HR function, including:
- Recruitment and selection
- Training and development
- Compensation and benefits
- Performance management
- Employee relations
HR managers must design context-specific HR policies that align global corporate objectives with local realities.
FAQs
What are inter-country differences in HRM?
They are variations between countries in culture, economy, labour costs, and industrial relations that influence HR practices.
Why do cultural differences matter in HRM?
Culture affects communication, leadership, motivation, and employee behaviour in the workplace.
How do labour costs affect international HRM?
Labour costs influence compensation strategies, location decisions, and workforce planning.
What role do trade unions play in HRM?
Trade unions influence wage negotiations, working conditions, and employee relations.
Can HR policies be standardized globally?
Only partially. HR policies must be adapted to local conditions while aligning with global strategy.