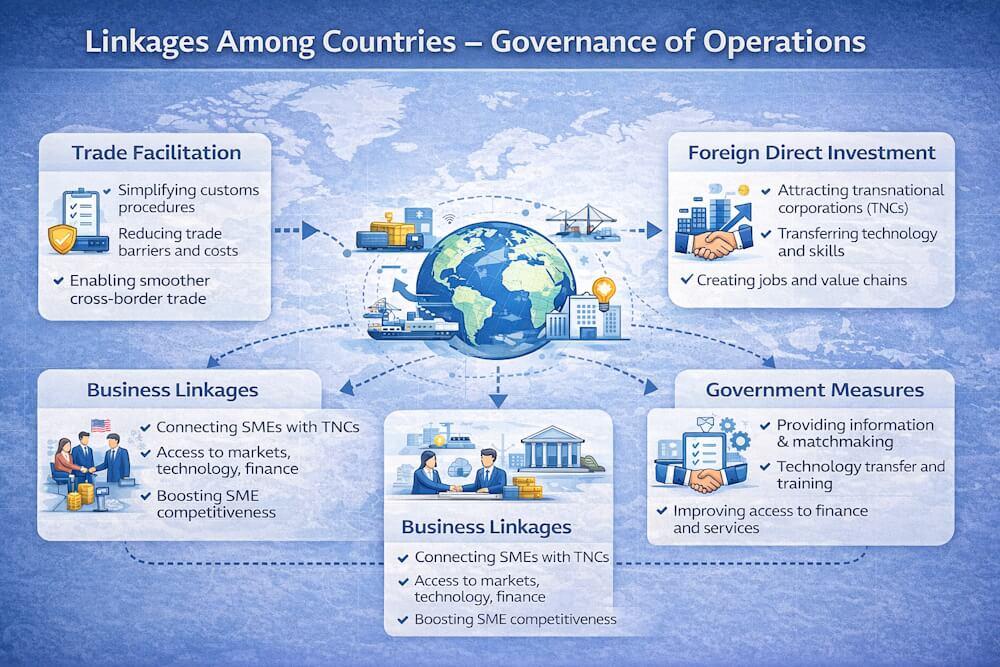
In recent years, trade facilitation—the removal of barriers to the cross-border movement of goods—has emerged as a critical factor in enhancing global trade and sustaining economic development. With growing trade volumes, complex procedures, and the expansion of global supply chains, effective governance of operations across countries has become essential.
Beyond reducing trade costs, trade facilitation promotes inclusive growth, enabling developing and least developed countries (LDCs) to integrate more effectively into the global economy.
Trade Facilitation and Global Governance
The global importance of trade facilitation was formally recognized with the adoption of the World Trade Organization (WTO) Trade Facilitation Agreement (TFA) in 2017. The agreement aims to:
- Simplify customs and trade procedures
- Reduce transaction costs
- Enable developing and LDCs to participate actively in global trade
- Use trade as a tool for economic growth and poverty reduction
The WTO TFA reflects the growing need for coordinated global governance mechanisms to manage international trade efficiently.
Role of Business Linkages in Economic Development
Research by UNCTAD highlights that business linkages are among the most effective ways for small and medium enterprises (SMEs) to enhance competitiveness. Through linkages with larger firms and transnational corporations (TNCs), SMEs gain access to:
- International markets
- Finance and investment
- Technology and innovation
- Management expertise and specialized knowledge
Over the past three decades, global experience has shown that markets alone are insufficient for sustained growth. Sound policies and strong institutions are equally important.
Government Policies and Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
In a globalized economy, governments must support development in open market environments rather than relying on protectionist policies. Foreign Direct Investment plays a key role in this process by:
- Transferring technology and skills
- Creating employment
- Integrating domestic firms into global value chains
However, expectations from FDI must be realistic. While TNCs can significantly contribute to development, their impact depends on effective governance, policy frameworks, and domestic absorptive capacity.
Measures to Promote Business Linkages
Strengthening domestic enterprises’ ability to absorb technology and knowledge is crucial. Governments and institutions can adopt several measures to promote effective linkages.
Key Government Measures to Strengthen Linkages
1. Provision of Information
Governments can act as facilitators by collecting and disseminating accurate information on linkage opportunities between domestic firms and foreign affiliates.
2. Matchmaking
Matchmaking requires active government involvement to connect buyers and suppliers based on specific capabilities and needs, helping firms establish sustainable supply relationships.
3. Technology Upgrading
Technological capability is a key determinant of supplier competitiveness. Governments may encourage:
- Technology transfer from TNCs to local firms
- R&D collaboration between domestic firms and research institutions
4. Technology Transfer Requirements
Policies may require TNCs to transfer technology not only to affiliates or joint ventures but also to local subcontractors.
5. Training and Skills Development
Training programs for SMEs and suppliers help strengthen interactions between foreign affiliates and domestic firms, improving workforce quality and productivity.
Additional Host-Country Support Measures
1. Promoting Supplier Associations
Government-supported supplier associations facilitate cooperation, training, and quality improvement among domestic firms.
2. Fostering Entrepreneurial Development
Entrepreneurship is a skill that must be nurtured through education and experience. UNCTAD’s Empretec Programme, for example, has supported over 120,000 entrepreneurs in 27 countries by providing:
- Entrepreneurial and managerial training
- Business planning support
- Access to domestic and international networks
3. Supporting Training Programs
Governments can collaborate with large firms, foreign affiliates, and international agencies to provide targeted training for SMEs.
Examples from India and Malaysia show how local managers in foreign affiliates helped build supplier networks by promoting local sourcing and skills development. Institutions such as the Penang Skills Development Centre play a vital role in upgrading supplier workforce capabilities.
4. Improving Access to Financial and Business Services
Limited access to finance is a major constraint for SMEs. Governments can support domestic firms by improving access to:
- Financial services
- Business development services
- Technical and managerial assistance
- Marketing and infrastructure support
India’s SME-focused policy initiatives aim to strengthen absorptive capacity and overcome development barriers.
5. Collaboration with International Agencies
International development agencies complement government efforts by supporting skills development, capacity-building, and enterprise growth in developing countries.
Governance of Operations in a Globalized World
Effective governance of global operations requires coordination between:
- Governments
- Transnational corporations
- SMEs
- Financial institutions
- International agencies
Together, these stakeholders help countries strengthen productive capacity, move up global value chains, and achieve sustainable and inclusive growth.
To understand how global linkages affect workforce management, read:
To explore how firms manage structural and HR challenges during international expansion, read:
These articles together create a strong interconnected content cluster on globalization, governance, and international business.
FAQs
What are linkages among countries?
Linkages among countries refer to economic, trade, and business connections formed through global value chains, FDI, and international partnerships.
Why is trade facilitation important?
Trade facilitation reduces costs, simplifies procedures, and enables smoother cross-border trade, especially for developing economies.
How do governments promote business linkages?
Governments use policies such as matchmaking, technology upgrading, training programs, financial support, and collaboration with international agencies.
What role do TNCs play in global linkages?
TNCs transfer technology, skills, and management expertise, helping domestic firms integrate into global markets.
Why are SMEs important in global supply chains?
SMEs enhance competitiveness, innovation, and employment when integrated into global value chains.